当居民依靠您以尽可能低的成本提供基本服务时,市政官员可能会觉得他们处于进退两难的境地。德克萨斯泰勒市通过将精益六西格玛应用于从垃圾收集到招聘过程的所有事务来解决这一难题。
该市在过去六年中已完成了 103 个项目,这些项目提高了居民的生活质量,同时节省了约 540 万美元。
例如,官员注意到 Westside 废水处理厂使用了不同量的氢氧化镁,这促使受过精益六西格玛培训的员工进行了调查。氢氧化镁可稳定 pH 水平、控制原始废水的气味、减少污泥并沉淀固体。
该团队着手确定满足所有必要功能的最佳氢氧化镁水平,并符合德克萨斯州环境质量委员会的 pH 水平要求。
挑战
Westside 废水处理厂处理该市约 60% 的废水,平均每天处理 750-800 万加仑。标准化废水中氢氧化镁的添加量将降低成本。项目团队首先需要确定导致波动的原因,并了解不同数量的化学品如何影响处理过的废水。

迄今为止,德克萨斯州泰勒市已通过精益六西格玛项目节省了超过 540 万美元,其中包括对该市 Westside 废水处理厂废水中添加的氢氧化镁数量进行标准化的项目。
在处理厂,员工将氢氧化镁与渠首的废水混合,在整个处理过程中达到所需的 pH 水平。每两小时取样一次,以确保符合州许可要求。
氢氧化镁成本高昂,因此员工寻求确保有效处理废水的最佳用量。他们评估了该系统并确定了几个过程变量,其中包括氢氧化镁剂量和入厂废水的碱度。
该团队需要测量每个变量以确定它们如何影响 pH 水平,并研究变量之间可能的相关性。碱度水平是否影响所需的氢氧化镁量? 氢氧化镁是否是提高和降低 pH 水平的唯一因素? 为了回答这些问题,项目团队使用了 Minitab Statistical Software。
Minitab 如何帮助他们
由于 Minitab 旨在让任何人都能访问统计信息,它消除了许多人对数据分析的恐惧。“Minitab 使员工能够轻松分析数据,”黑带大师兼泰勒市管理人员 Guillermo Garcia 说道。例如,Assistant 功能指导团队成员完成分析,即使他们以前从未使用过该软件。
项目团队使用 Minitab Statistical Software 生成回归方程,该方程描述变量与响应之间的关系,并以图形方式显示数据。这些结果帮助他们看到氢氧化镁与碱度和 pH 水平之间的关系。Garcia 说:“这些图像让我们清楚地了解了数据告诉我们的内容。
在跟踪氢氧化镁剂量随时间的变化范围后,该团队确定来料废水中的低碱度周期是化学剂量增加的原因。员工最初认为,添加更多氢氧化镁可以纠正低碱度。现在他们知道了为什么处理会发生波动,该团队就可以专注于测试碱度和 pH 水平,以确定是否真的需要额外的氢氧化镁。
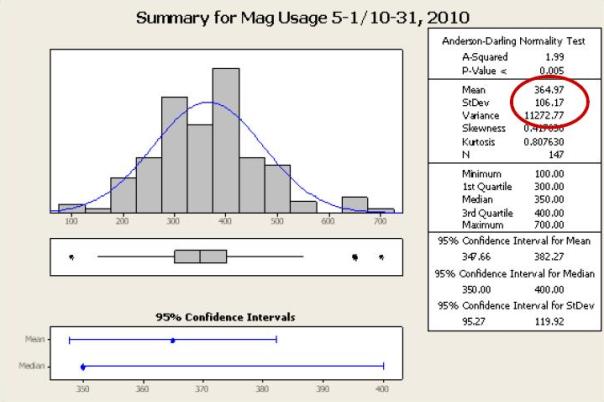
上面的图形汇总显示了添加到废水中的氢氧化镁水平的变化。
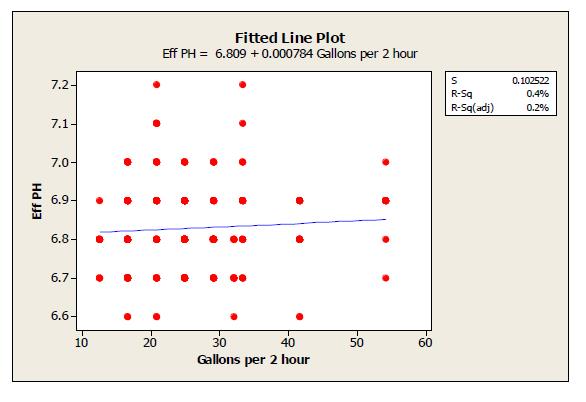
上面的拟合线图反映:随氢氧化镁剂量每两个小时从低至 12 加仑波动到高达 55 加仑 pH 水平无显著变化。
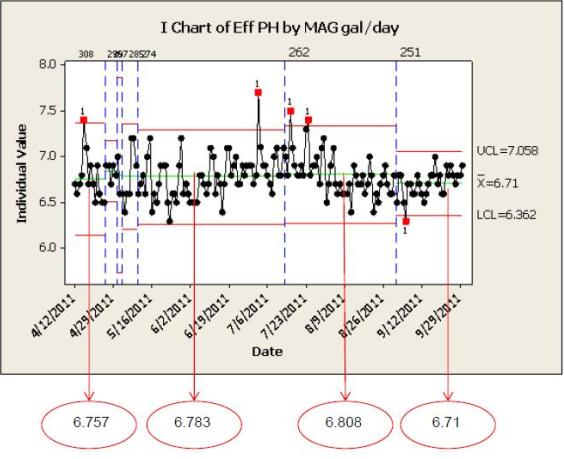
此 I 控制图显示,在团队确定氢氧化镁的理想使用量后,pH 样本结果变化很小。
该团队的分析表明,添加氢氧化镁几乎不会改变废水的碱度和 pH 水平。根据这些结果,该团队确定了向废水中添加的理想氢氧化镁量,他们使用 Minitab 的控制图来验证和说明他们取得的成功。
结果
数据分析显示,氢氧化镁剂量基本上不影响 pH 水平或纠正低碱度。该设施可以稳定剂量并降低成本,同时完全确信处理后的废水仍将符合州法规。氢氧化镁的变化量从每天 106.17 加仑减少到 15.57 加仑。该项目的节省额超过了最初估计的美元金额,迄今为止总计超过了 79,000 美元。Westside Wastewater Treatment Plant 还制定了标准操作程序,在确保过程持续有效的同时,为该市及其纳税人节省资金。
正如该市居民所知,这只是许多改进项目之一,其好处确实在不断增加。Barbara Bass 市长表示:“我们所有的绿带和黑带都已完成专注于改进城市过程的项目,从而节省了时间或金钱。”
“我相信,我们的成功可以归功于我们的精益六西格玛计划与其他员工参与战略的协同作用。”城市经理 Mark Daniel 说道。“到目前为止,该市项目的累计节省超过 540 万美元。”

组织
德克萨斯州泰勒市
概述
- 人口约为 107,405
- 区域教育和技术中心
- 由于它在玫瑰种植行业中的作用,并拥有美国最大的市政玫瑰园,因此被称为“世界玫瑰之都”
挑战
提供卓越的公共服务,同时尽可能降低市政成本。
采用的产品
Minitab® Statistical Software
结果
- 使用精益六西格玛完成城市的 103 个项目
- 总节省超过 540 万美元
- 例如,到目前为止,废水处理厂的优化氢氧化镁工艺节省了 79,000 多美元



